Definition and source of phytase
Phytase, also known as inositol hexaphosphate hydrolase, belongs to the orthophosphate monoester phosphate hydrolase family, which can hydrolyze phytate into some inositol derivatives.
Phytase exists widely in nature. It can be divided into 3-phytase, 4/6-phytase and 5-phytase according to the different positions of the phosphate groups on the inositol ring of phytase hydrolyzing phytic acid molecules. Each phytase is not only structurally different, but also has different hydrolysis mechanisms. 3-Phytase can hydrolyze the phosphate ester bond of phytic acid position 3, usually from microorganisms; 4/6-Phytase can hydrolyze the phosphate ester bond at D4 or L6 position, which usually exists in the seeds of higher plants; 5-Phytase can hydrolyze phytic acid υ- The phosphate ester bond at position 5 is usually found in ruminant lunata, alfalfa and legumes.
Phytase widely exists in plants, animals and microorganisms in nature. Because the activity of phytase in animals and plants is relatively low and it is difficult to separate, people are more committed to microbial research to seek industrial application. In the past 20 years, several bacterial, yeast and fungal strains can be applied on an industrial scale to produce high yield phytase. At the same time, people are also trying to use a variety of means to purify phytase and study the expression of phytase in the host
Phytate and its characteristics
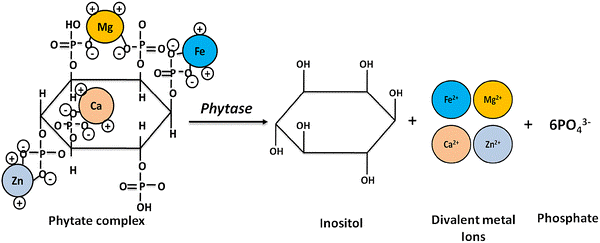
Phytate, chemically known as inositol hexaphosphate, is a combination of 1-molecule inositol and 6-molecule phosphoric acid, which is the main storage form of phosphorus in plants. Many of the plants such as corn, grains, seeds, legumes, soybeans and most cereals contain high amounts of this acid. Referred to as an “anti-nutritional factor,” these phytates (phytic acid) reduce the ability to absorb nutrients.
Phytic acid phosphorus has a very stable structure and strong chelating ability. It can form stable chelates with divalent metal ions such as Ca2+, Fe2+, Mg2+, Zn2+,Cu2+, M2+, etc., thus affecting the absorption of mineral elements.
Phytase activity depends on pH and temperature
The optimal temperature of plant phytase is generally between 30~60 ℃, and the optimal pH is 4.0~7.2. Relatively speaking, the application value of plant phytase after separation and purification is not high. Because the acid environment in the stomach of monogastric animals is lower;The pH value of phytase from microorganisms ranges from 2.5 to 6.0, which can adapt to the strong acid environment in the stomach and the weak acid environment in the intestine of animals. Therefore, microbial phytase has been used in industrial production and is mostly used as animal feed additive.
Application
Phytase is an enzyme that has the ability to liberate the phosphate and mineral residues from phytic acid (phytate). Phytic acid is an excellent source of carbon, nitrogen, and sulfur that may be converted into a range of chemicals in the natural world. it has a wide range of industrial, agricultural, and biotechnological uses due to their ability to break down keratins.
➢ Feed Supplements
Monogastric animals, like pigs, poultry, and fish, have no or low amounts of gastrointestinal phytases, preventing them from using the Phytic acid phosphorus found in food and livestock feed. As a result, they require inorganic phosphate supplementation to satisfy their dietary and growth requirements, which raises feed costs and phosphorus pollution levels.
➢ Food Additives
Phytic acid is highly abundant in the grain and wholewheat flour of many types of bread and dough, hence phytases are utilized as a food additive in fermentation processes and in a variety of applications in the production of bread.
➢ Plant Growth Promoter
Phosphorus is a key and essential component of plant cells, and it plays a role in energy metabolism and cell membrane biosynthesis. This is also a key macronutrient for plant growth and developmental processes. Soil phosphorus shortage is a big issue for agricultural farmers all over the world. The majority of soils contain considerable levels of total soil P, which may be found in both organic and inorganic forms. Phytic acid is a primary source of biological phosphorus in the soil, accounting for 10 to 50% of available organic phosphorus content. So, the phytase enzyme is essential to digest it.
➢ Therapeutic Applications
Humans use plant-based food items as their primary source of raw component nutrition in many regions of the globe. Plant-based foods are rich in nutrients (carbohydrates, protein, fibre, and vitamins), as well as non-nutrients. Phytate is the most important phosphorus storage molecule in seeds and grains, accounting for up to 90% of overall seed phosphorus. It creates a mineral shortage in humans by forming a complex with dietary elements such as zinc, iron, calcium, magnesium, manganese, and copper.
➢ Waste disposal
Reducing phosphorus containing waste is more beneficial to the earth. Too much phosphorus eventually seeps into groundwater, lakes and streams. Algae multiply in the presence of phosphorus, deplete oxygen in the water, destroy plants and damage the local ecosystem.
Lessening waste items containing phosphorus is additionally better for the earth. Phosphorus contained waste in the end filters into groundwater, lakes, and streams. Algae flourish with phosphorus and multiply in its presence, which exhausts the quantity of oxygen in the water, destroying plants and compromising the local ecosystem.
Key Reference
1. phytase







